September 2018 Issue
Research Highlights
Next Generation Router Architecture: Packet Processing Prediction
Recently, dramatic increases in the volume of internet traffic has become a serious problem for routers due to strict demands for high throughput. To make matters worse, it is reported that the total power consumption of network devices is expected to reache several percentage of the total power generated in the world. Hence routers must achieve higher throughput with lower power consumption.
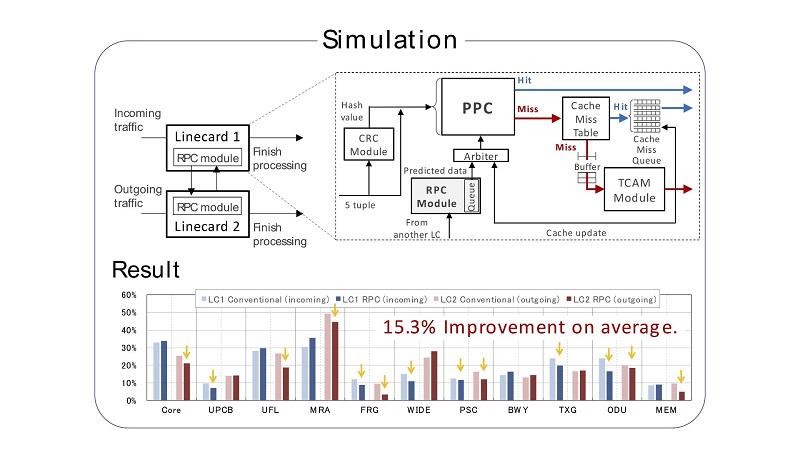
Packet Processing Cache (PPC) is a promising approach to meet these requirements. PPC stores packet processing results into a cache memory, which is a small but high-speed and low-power memory, and reuses the cached results to process the following packets. For PPC, it is important to process as many packets as possible by using the cached results and bypassing conventional packet processing.
Yamaki and colleagues at the University of Electro-Communications, Tokyo, have proposed the novel caching strategy for PPC, called Response Prediction Cache (RPC). RPC predicts the response packets and the processing results based on the request packets and stores them into the cache in advance. By using RPC, routers can process packets before their arrival.
RPC predicts responses based on the request packets and stores them into the cache in advance. By using RPC routers can process packets before their arrival.
RPC increases the packet processing throughput by 5.02x and reduces the power consumed to process a packet by 75%.
"Packet Processing prediction is a novel approach for routers. If more packets can be processed by this approach, then routers can achieve significantly higher power efficiency," says Yamaki.