March 2016 Issue
Research Highlights
Environmentally friendly refrigerant measures up
The fluid flow and heat transfer characteristics of refrigerants in narrow tubes is important for designing heat exchangers for air-conditioning systems. While standard refrigerants have been well investigated, environmental concerns have prompted the development of refrigerants with lower global warming potential, and the properties of these alternatives have been less well studied so far. A collaboration of researchers in Japan has now reported on the refrigerant R32, which has a low global warming potential.
A previous report had suggested a much better heat transfer coefficient for R32 compared to another refrigerant that had higher global warming potential, that is, R410A. A number of parameters can affect heat transfer coefficients, including the tube diameter, heat flux and vapour quality - the mass fraction in a saturated mixture that is vapour. These affect the type of heat transfer, which include flow boiling, liquid film evaporation, nucleate boiling and forced convection.
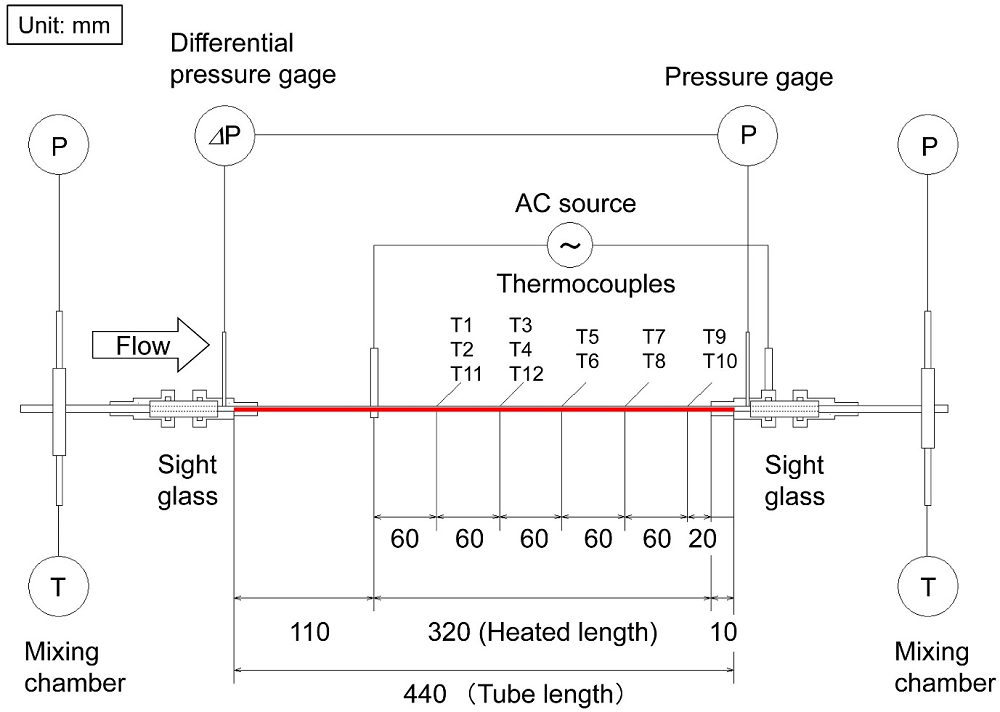
The work was the collaboration of Yudai Matuse at the Hitachi Zosen Corporation, Koji Enoki at the University of Electro-Communications (the affiliation when this paper published was Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology), Hideo Mori and Yoshinori Yamamoto at Kyushi University, and Keishi Kariya at Saga University. They monitored heat transfer, pressure drop and the phase flow pattern of R32 in a copper tube with an inside diameter of 1.0 mm. They compared the results with another refrigerant R410A, which had been extensively reported on previously.
The researchers concluded, "The liquid film evaporation heat transfer was predominant at low quality or low mass flux in a low heat flux condition." The measured heat transfer data also raised questions with respect to predictions from other studies.
Reference
Yudai Matsuse1, Koji Enoki2, Hideo Mori3, Keishi Kariya4 & Yoshinori Hamamoto3 Boiling Heat Transfer and Pressure Drop of a Refrigerant R32 Flowing in a Small Horizontal Tube, Heat Transfer Engineering, (2016) doi: 10.1080/01457632.2015.1067057.
- Plant Design and Engineering Department, Hitachi Zosen Corporation, Osaka, Japan
- Institute of Engineering, Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology, Koganei, Japan (Present affiliation is the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Intelligent System, University of Electro-Communications)
- Department of Mechanical Engineering, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan
- Department of Mechanical Engineering, Saga University, Saga, Japan