September 2015 Issue
Research Highlights
Motor behaviour: understanding the jerks that lurk in smooth movements
Apparently smooth continuous movements to trace moving objects harbour jerks. These jerks are absent when there is no object to be traced and so are thought to stem from changes in motor instructions anticipated and fed forward by the brain to compensate for sensorimotor time lags. However so far there is no conclusive evidence that this is the case. Now Yasuyuki Inoue and Yutaka Sakaguchi at the University of Electro-communications have demonstrated a method for analysing apparently smooth movements that may help to understand their jerky components.
"The true purpose of detecting discontinuities is to know when and how our brain divides a continuous motor task into separate movement segments," explain Inoue and Sakaguchi in their report. While studies of intermittency have been tackled using frequency analysis of the velocity profiles, the intervals between the intermittent motor discontinuities vary, so this may not be appropriate.
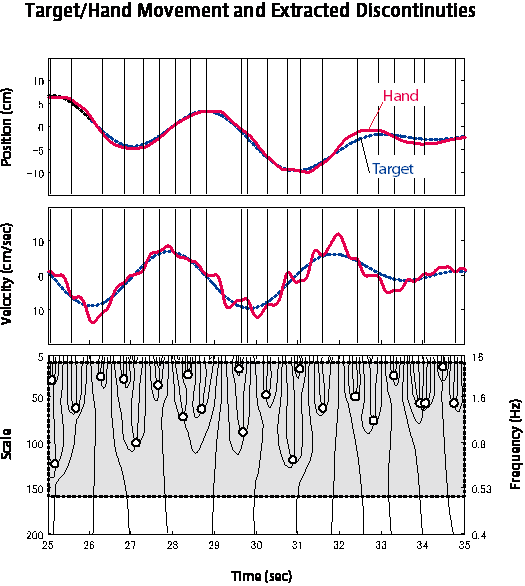
Another approach is to extract the sub-movements that comprise apparently continuous motion by identifying the discontinuities. However the methods to do this - using kinematic parameters and curve fitting optimisation - become unmanageable for long movements.
Inoue and Sakaguchi show that continuous wavelet transforms are an effective means of identifying discontinuities without suffering the drawbacks of other approaches for longer movements. They also show how to distinguish the discontinuities from other movement features such as hand tremors or peaks in a pulse of movement.
"Our method is essentially equivalent to detecting the jerk change points, but it uses both the amplitude and phase information of the complex wavelet transform to much improve detection performance," explain Inoue and Sakaguchi in their report. They successfully detected all the discontinuities in an artificial data set with no false detections, as well as demonstrating their approach on human subjects asked to trace a moving object with their hand.
Reference
- Inoue Y, Sakaguchi Y A wavelet-based method for extracting intermittent discontinuities observed in human motor behavior Neural Networks 62: 91-101 (2015)
doi:10.1016/j.neunet.2014.05.004