Topics - e-Bulletin
University of Electro-Communications publishes September 2017 issue of e-Bulletin
The September 2017 issue of the UEC e-Bulletin includes a feature article about research by Takuji Koike on his "quest to find effective solutions to support people with hearing loss".
The Topics section focuses on the convergence of science and art, focusing on the work by artist and UEC Tokyo associate professor Sachiko Kodama's on her rendering of dynamic, three dimensional sculptures using magnetic 'ferrofluids'.
Research highlights from high impact publications are 'Radar for environmental monitoring: new algorithms for high speed and low cost 3D imaging', Shouhei Kidera; 'Astronomical spectroscopy in a laboratory: Direct and accurate measurements of electron densities of plasmas', Erina Shimizu and Safdar Ali; 'Nanophotonics: Integrating nanocavities into optical fibers with femtosecond laser ablation', Kohzo Hakuta; 'Two dimensional materials: Advanced molybdenum selenide near infrared phototransistors', Abdelkader Abderrahmane; and 'Laser science: Innovative solid state lasers with Yb3+-doped CaF2 - LaF3 ceramic gain media', Shotaro Kitajima and Hitoshi Ishizawa.
Feature
Frontiers of audiology: Quest to find effective solutions to support people with hearing loss
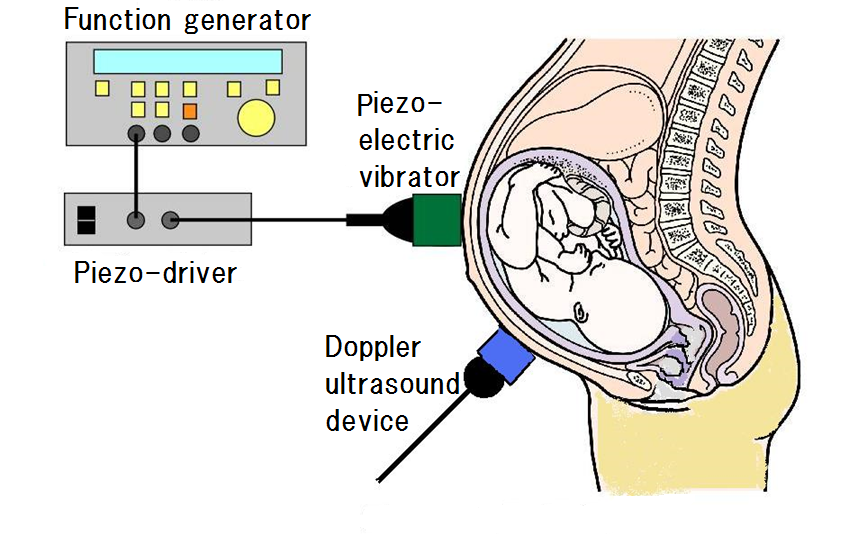
Takuji Koike is collaborating with medical doctors in Japan to clarify the origins of auditory problems as well as developing devices to support people suffering from hearing loss. "We are focusing on three main areas," says Koike. "Gaining insights into the mechanisms governing hearing disorders for the development of effective treatments; measuring the response of fetuses to sound; and developing hearing aids that are implanted into the bone behind the ear."
Research Highlights
Radar for environmental monitoring: New algorithms for high speed and low cost 3D imaging
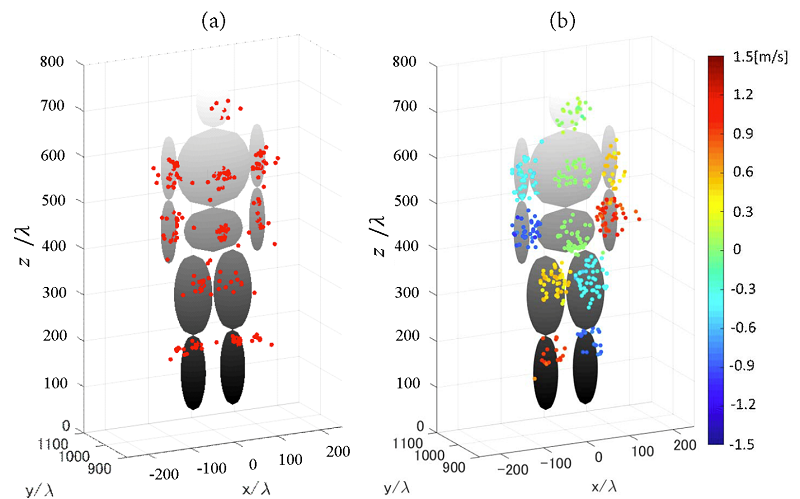
Ultrawideband millimeter-wave radar devices are promising as high precision sensors to monitor environments where vision is hindered due to clouds and fog for applications including automobile collision avoidance systems. Importantly, during the identification of objects under such circumstances, raw data from the sensors must be rapidly and accurately processed into three dimensional images by so-called 'conversion algorithms'.
Astronomical spectroscopy in a laboratory: Direct and accurate measurements of electron densities of plasmas
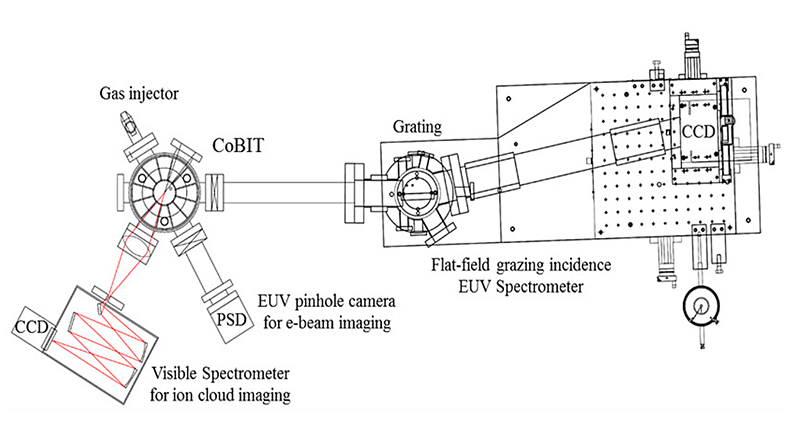
Isaac Newton's discovery in the mid-1600s that white light consists of a 'spectrum' of rainbow colors, and then in the early 1800s Joseph von Fraunhofer's observation of lines in the solar spectrum laid the foundations for modern day spectroscopy—the workhorse of astronomers analyzing the chemical compositions of plasmas that form the basis of stars and galaxies.
Laser science: Innovative solid state lasers with Yb3+-doped CaF2 - LaF3 ceramic gain media
http://www.ru.uec.ac.jp/e-bulletin/research-highlights/2017/laser-science.html

Polycrystalline ceramic materials offer advantages including robustness over conventional glass as gain media for solid state lasers: devices that find many applications such as laser processing and medical surgery.
Two dimensional materials: Advanced molybdenum selenide near infrared phototransistors
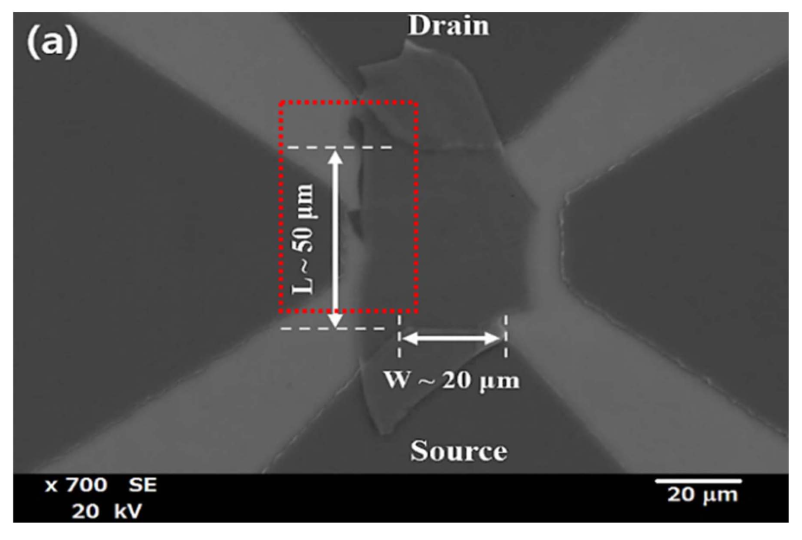
Optical sensors operating in the near infrared (NIR) are important for applications in imaging, photodetectors, and biological sensors. Notably, recent reports on the synthesis of high quality, large areas of graphene has motivated researchers to search for other 2D materials with properties suitable for NIR devices.
Nanophotonics: Integrating nanocavities into optical fibers with femtosecond laser ablation
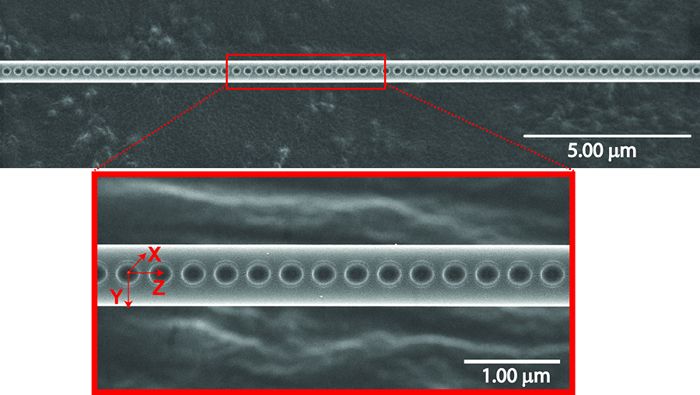
Controlling and manipulating the interaction of light with nanostructures offers the promise of new and innovative technological applications ranging from nanolasers and sensors to quantum computing. However, in spite of tremendous advances in nanotechnology that has enabled the fabrication of one and two dimensional structures (such as photonic crystal cavities), efficiently integrating nanocrystal cavities with modern optical fibers in communications networks is proving to be difficult.
Topics
Convergence of science and art: Three dimensional dynamics of ferrofluid sculptures
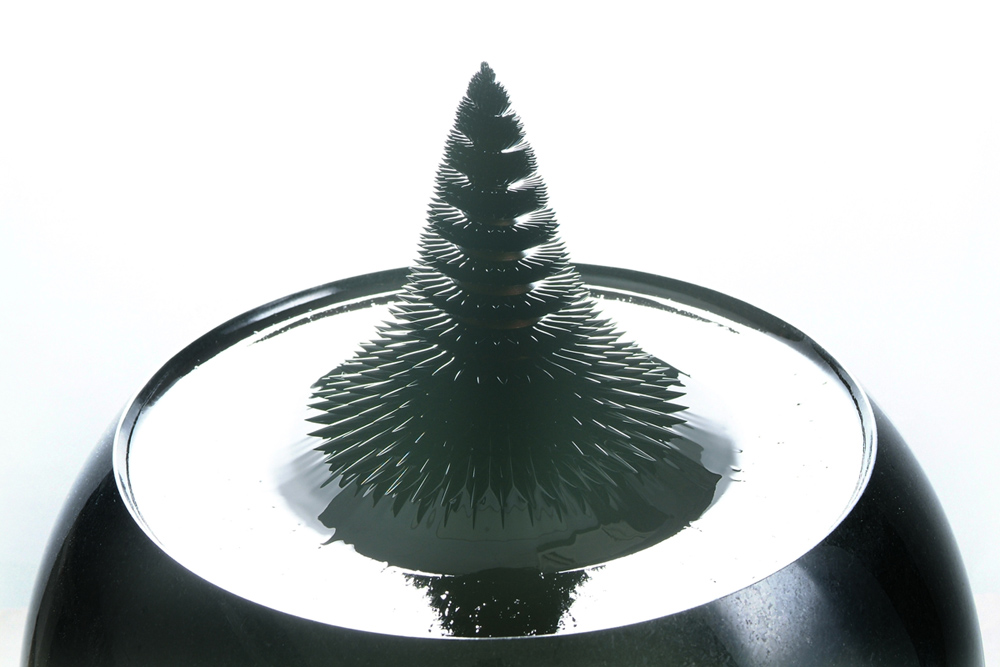

Sachiko Kodama is an artist internationally recognized for her renderings unique and dynamic three dimensional sculptures including "Protrude Flow" (2001), "Morpho Tower" (2006), and "Pulsar" (2008) by controlling the intricate interaction of magnetic field lines with solutions of dark and optically reflective ferrofluids.

